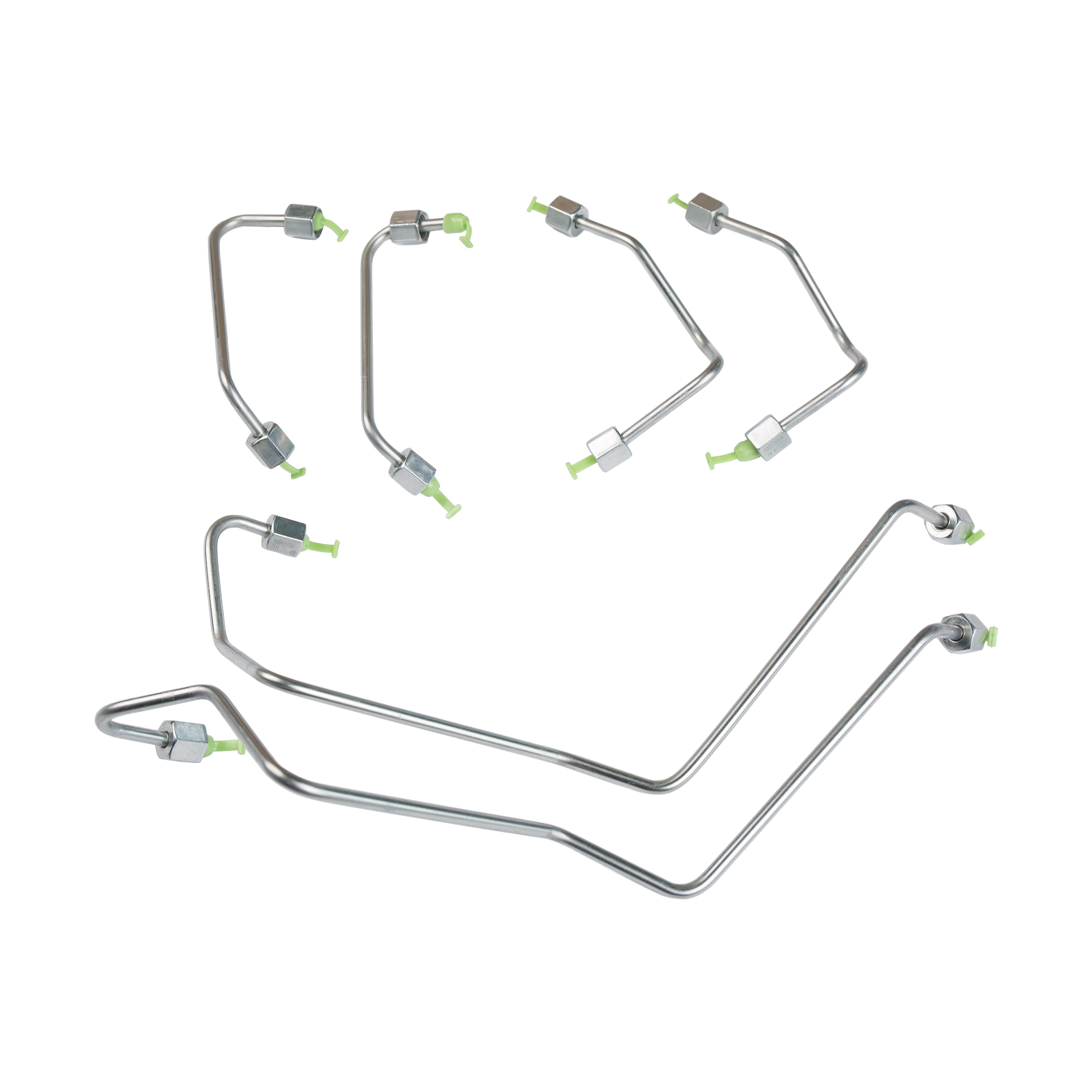
Low-pressure oil pipes are an essential component of an engine’s lubrication system. They transport oil from the oil pump to various engine parts, ensuring smooth operation, reducing friction, and preventing wear. For vehicle owners, mechanics, and manufacturers, a common question arises: is an engine low-pressure oil pipe suitable for gasoline engines, diesel engines, or both? To answer this, we need to consider the differences between engine types, operating conditions, and the design characteristics of low-pressure oil pipes.
1. Understanding Low-Pressure Oil Pipes
Low-pressure oil pipes are designed to handle the circulation of lubricating oil under relatively low pressure, typically from the oil pump to bearings, camshafts, and other engine components. Unlike high-pressure oil pipes used in fuel injection systems or turbocharger lubrication lines, low-pressure oil pipes do not need to withstand extremely high pressures.
Key features include:
Durability: They are made of materials resistant to oil, heat, and corrosion, such as reinforced rubber, silicone, or metal composites.
Flexibility: Low-pressure oil pipes can bend and route through the engine compartment without kinking.
Oil Compatibility: These pipes are designed to work with engine oils of different viscosities used in gasoline or diesel engines.
2. Gasoline Engines vs. Diesel Engines
Gasoline and diesel engines have some differences that affect the design of low-pressure oil pipes:
Operating Temperature: Diesel engines typically operate at higher temperatures and pressures than gasoline engines, which may require slightly more heat-resistant materials.
Oil Viscosity: Diesel engines often use higher-viscosity oils to handle higher loads, while gasoline engines may use lighter oils for efficiency.
Engine Design: Diesel engines generally have stronger components to handle higher compression ratios, which may slightly increase oil flow requirements.
Despite these differences, low-pressure oil pipes are designed to accommodate standard lubrication conditions in both engine types. Manufacturers test their pipes for a wide range of oil viscosities, temperatures, and flow rates to ensure universal compatibility.
3. Material and Design Considerations
To be suitable for both gasoline and diesel engines, low-pressure oil pipes must meet certain criteria:
Heat Resistance: Materials like reinforced silicone, high-temperature rubber, or stainless steel can withstand the higher temperatures in diesel engines.
Chemical Resistance: Pipes must resist degradation from engine oils, additives, and potential contaminants.
Pressure Rating: Although these are low-pressure lines, they must handle occasional pressure spikes safely without leaking or bursting.
Flexibility and Strength: The pipe must be flexible enough to fit engine layouts while maintaining structural integrity.
Many modern low-pressure oil pipes are designed with these features, allowing them to be used interchangeably in gasoline and diesel engines for most passenger cars, trucks, and industrial engines.
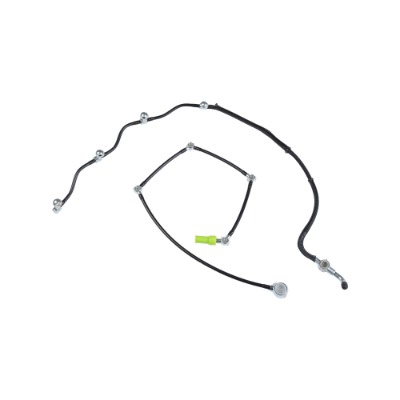
4. Advantages of Using Low-Pressure Oil Pipes in Both Engine Types
Using properly designed low-pressure oil pipes for either gasoline or diesel engines provides several benefits:
Reliable Lubrication: Ensures consistent oil delivery, reducing friction and wear on critical engine components.
Maintenance Convenience: Universal compatibility reduces the need for multiple part numbers and simplifies inventory for garages and repair shops.
Cost Efficiency: Manufacturers can produce standardized pipes suitable for both engine types, lowering production and logistics costs.
Durability: High-quality low-pressure oil pipes resist heat, oil, and environmental factors, ensuring long service life in both engine types.
5. Installation and Maintenance Tips
Even though low-pressure oil pipes are suitable for both gasoline and diesel engines, proper installation and maintenance are important:
Correct Routing: Avoid sharp bends or contact with hot surfaces to prevent damage.
Secure Fittings: Ensure clamps and connections are tight to prevent leaks.
Regular Inspection: Check for cracks, bulges, or signs of wear, especially in high-temperature areas.
Use Compatible Oil: Always use the recommended oil type and viscosity for the engine to prevent pipe degradation.
Replace When Necessary: Although low-pressure oil pipes are durable, they should be replaced if any signs of wear, leakage, or hardening appear.
6. Common Applications
Low-pressure oil pipes are used in a wide variety of engines:
Gasoline Engines: Passenger cars, motorcycles, small trucks, and light-duty vehicles.
Diesel Engines: Trucks, buses, industrial machinery, generators, and marine engines.
Hybrid Engines: Both gasoline and diesel hybrid engines can use compatible low-pressure oil pipes for lubrication lines.
This versatility demonstrates the universal design of modern low-pressure oil pipes.
Is the engine low-pressure oil pipe suitable for gasoline or diesel engines? The answer is yes. Properly designed low-pressure oil pipes are compatible with both engine types. They are engineered to handle varying oil viscosities, temperature ranges, and operating conditions found in gasoline and diesel engines.
The key is to select high-quality pipes made from durable, heat-resistant, and oil-compatible materials. With proper installation, maintenance, and inspection, low-pressure oil pipes ensure reliable lubrication, protect engine components, and extend engine life, whether in a gasoline-powered sedan or a diesel-powered truck.
In summary, modern engine low-pressure oil pipes are a versatile, reliable, and essential component suitable for a wide range of internal combustion engines.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский