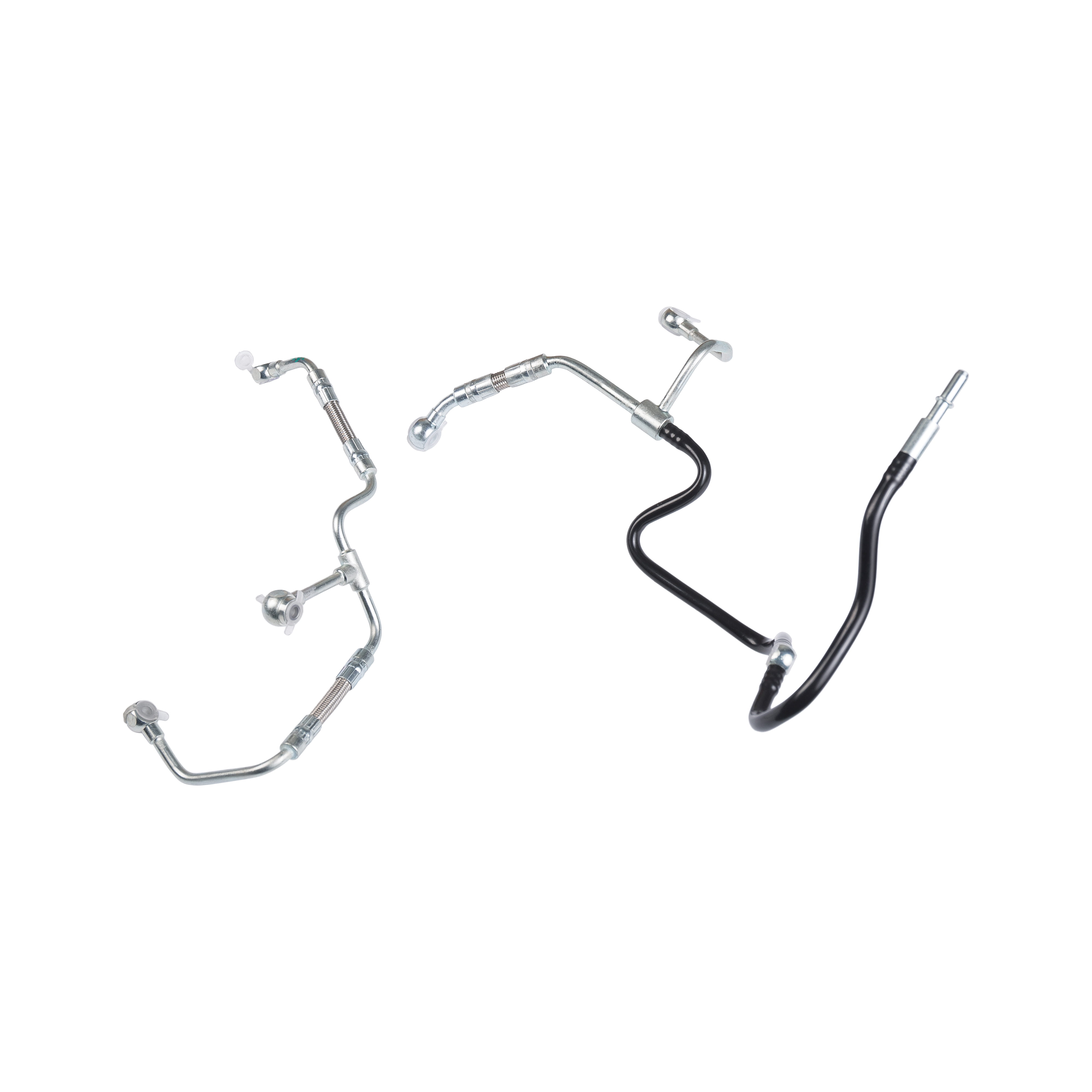
1. Introduction to Low-Pressure PTFE Engine Oil Pipes
Low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipes are widely used in automotive and industrial engines to transport engine oil safely and efficiently. Made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), these pipes offer excellent chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low friction, making them ideal for lubricating systems. Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure long-term performance, prevent leaks, and avoid engine damage.
2. Regular Inspection of PTFE Engine Oil Pipes
Frequent inspections help identify early signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Maintenance personnel should pay attention to the following aspects during inspections:
2.1 Visual Inspection
- Check for cracks, abrasions, or deformations along the pipe surface.
- Look for signs of oil leakage at connection points or along the pipe length.
- Ensure that clamps, fittings, and connectors are secure and free from corrosion.
2.2 Pressure and Flow Monitoring
Although these pipes are designed for low-pressure applications, monitoring oil pressure and flow is essential. Sudden drops or fluctuations can indicate a blockage, internal wear, or partial collapse of the PTFE lining, which requires immediate attention.
3. Cleaning and Contamination Prevention
Maintaining cleanliness is critical for the longevity of PTFE engine oil pipes. Contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, or degraded oil can reduce the pipe’s efficiency and potentially damage the engine.
3.1 Internal Cleaning
- Flush the pipes with clean engine oil or a compatible solvent to remove sludge and debris.
- Use low-pressure cleaning methods to prevent damage to the PTFE lining.
3.2 External Cleaning
- Wipe the outer surface with a lint-free cloth to remove dust and oil residues.
- Avoid harsh chemical cleaners that can affect pipe flexibility or fittings.
4. Proper Installation Practices
Correct installation is essential for preventing leaks, kinks, and premature wear. PTFE pipes require specific handling techniques due to their flexible and slippery nature.
4.1 Avoiding Excessive Bending
Ensure that the pipe radius exceeds the minimum bending radius specified by the manufacturer. Sharp bends can damage the internal PTFE lining and reduce flow efficiency.
4.2 Secure Fittings and Clamps
Use appropriate clamps and connectors to prevent movement or vibrations. Loose fittings can cause leaks and increase mechanical stress on the pipe.
4.3 Alignment and Support
Ensure that pipes are aligned properly and supported to reduce stress from engine vibrations. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear and eventual failure.
5. Temperature and Pressure Considerations
PTFE engine oil pipes are designed to withstand low-pressure applications, but extreme temperatures can still affect their performance.
5.1 Operating Temperature
Avoid exposure to temperatures beyond the manufacturer’s recommended range. Excessive heat can soften fittings, reduce flexibility, and increase the risk of oil leakage.
5.2 Pressure Monitoring
Even in low-pressure systems, sudden spikes can damage the pipe. Regularly monitor engine oil pressure and ensure safety valves or regulators are functioning correctly.
6. Storage and Handling Tips
Proper storage and handling prolong the life of PTFE engine oil pipes before installation or during maintenance cycles.
6.1 Storage Conditions
- Store pipes in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Avoid exposure to strong UV sources or chemicals that can degrade pipe material.
6.2 Handling Precautions
- Handle pipes gently to avoid kinks, scratches, or contamination.
- Use protective gloves when cutting or connecting pipes to maintain cleanliness.
7. Replacement and End-of-Life Indicators
Despite proper maintenance, PTFE engine oil pipes eventually reach the end of their service life. Identifying signs of wear is essential for safety and engine protection.
7.1 Signs of Wear
- Visible cracks, bulges, or abrasions on the pipe surface
- Persistent oil leaks around fittings or along the pipe
- Loss of flexibility or kinking under normal operating conditions
7.2 Recommended Replacement Intervals
Manufacturers usually provide guidelines for replacement intervals based on engine type and operating conditions. Adhering to these recommendations ensures continued engine performance and prevents unexpected failures.
8. Conclusion
Maintaining low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipes involves regular inspections, proper cleaning, careful installation, temperature and pressure monitoring, and correct storage. Paying attention to these factors extends pipe life, ensures safe engine operation, and prevents costly repairs. By following recommended maintenance practices, PTFE engine oil pipes can deliver reliable performance in low-pressure lubrication systems over the long term.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский