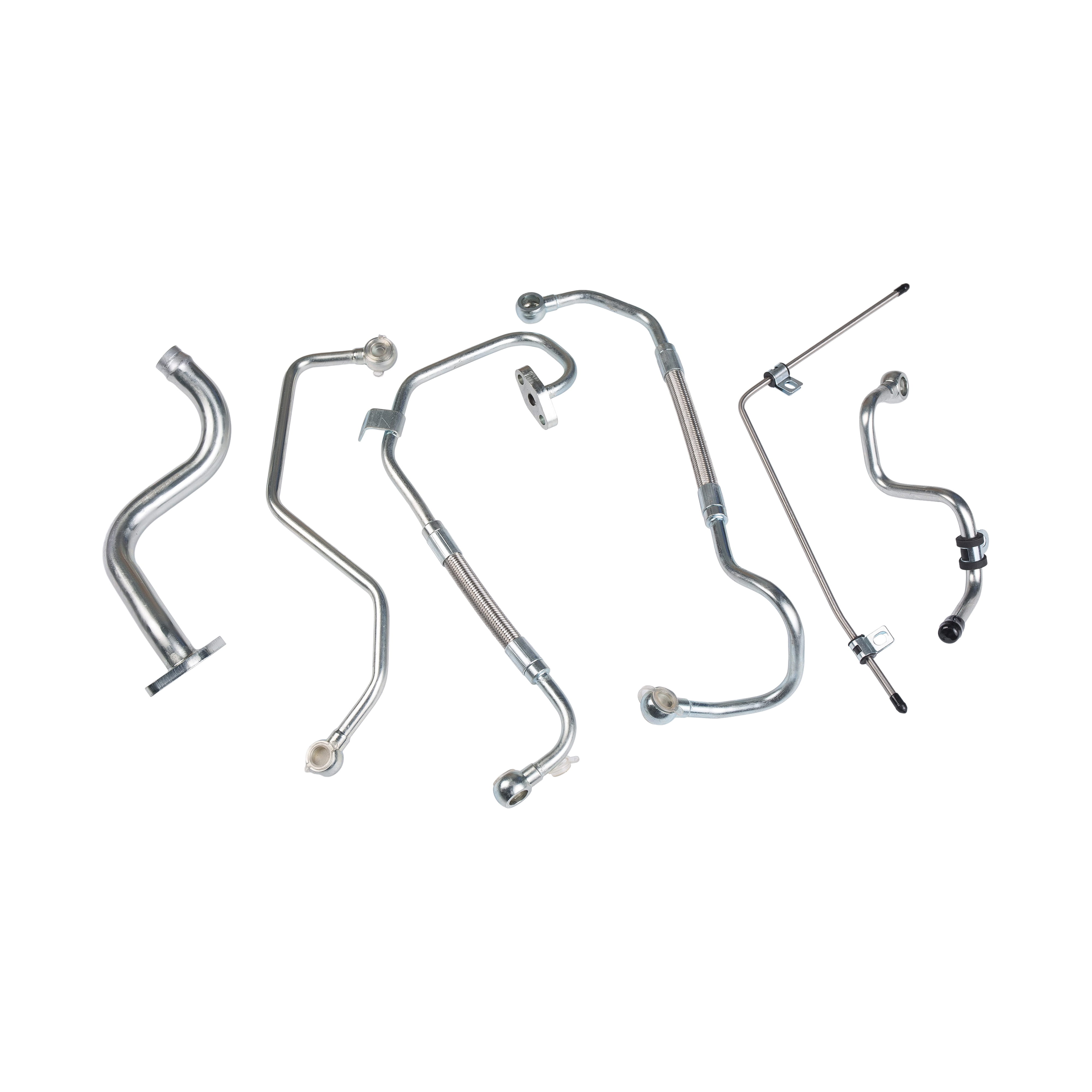
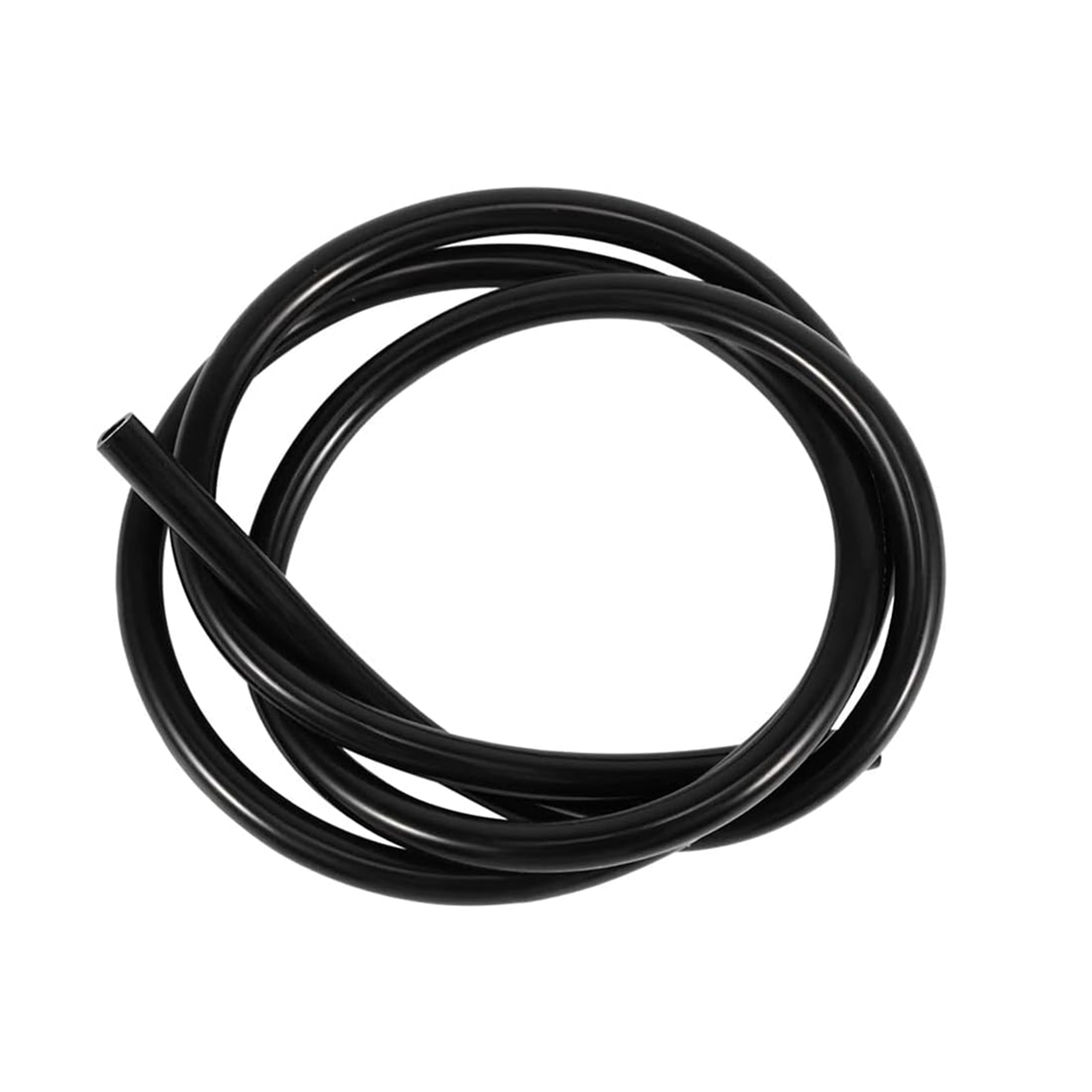
Overview of Low-Pressure PTFE Engine Oil Pipes and Rubber Oil Hoses
Low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipes and rubber oil hoses are both widely used for transporting engine oil in automotive and industrial systems. While they serve a similar basic function, their material properties, performance characteristics, and long-term reliability differ significantly. Understanding these differences is critical when selecting the right oil transfer solution for specific operating conditions.
A low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipe is typically made from polytetrafluoroethylene, a high-performance polymer known for its chemical stability and temperature resistance. In contrast, a rubber oil hose is generally composed of synthetic rubber compounds reinforced with textile or steel layers, designed for flexibility and cost efficiency.
Material Composition and Structural Differences
The most fundamental difference between a low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipe and a rubber oil hose lies in their material composition. PTFE is a fluoropolymer with a tightly bonded molecular structure, resulting in excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and aging. Rubber hoses rely on elastomeric materials that provide flexibility but are more susceptible to environmental degradation.
Structurally, PTFE oil pipes often include a smooth inner liner and may be reinforced with braided stainless steel or synthetic fibers, even in low-pressure applications. Rubber oil hoses typically consist of an inner rubber tube, a reinforcement layer, and an outer protective cover.
Impact on Oil Flow and Cleanliness
The inner surface of a PTFE engine oil pipe is extremely smooth, reducing friction and minimizing oil residue buildup. Rubber hoses, by comparison, can degrade internally over time, potentially releasing particles into the oil system.
Temperature Resistance and Thermal Stability
Temperature resistance is one of the most significant advantages of a low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipe. PTFE can typically withstand continuous operating temperatures far higher than standard rubber compounds without hardening, cracking, or losing structural integrity.
Rubber oil hoses are more limited in this regard. Prolonged exposure to high engine temperatures can cause rubber to soften, harden, or develop micro-cracks, ultimately leading to leaks or failure.
Performance in Engine Compartments
In tightly packed engine bays where heat accumulation is common, PTFE oil pipes maintain stable performance. Rubber hoses may require heat shields or more frequent replacement under similar conditions.
Chemical and Oil Resistance
Low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipes exhibit exceptional resistance to engine oils, synthetic lubricants, fuel vapors, and additives. PTFE does not react chemically with most automotive fluids, ensuring consistent performance over long service intervals.
Rubber oil hoses are designed to be oil-resistant, but their resistance varies depending on the rubber formulation. Over time, exposure to aggressive additives and high temperatures can cause swelling, softening, or loss of elasticity.
- PTFE resists oxidation and chemical breakdown
- Rubber may degrade when exposed to modern synthetic oils
- PTFE maintains oil purity over long-term use
Flexibility and Installation Considerations
Rubber oil hoses are generally more flexible than low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipes, making them easier to route in complex or confined spaces. This flexibility allows for quick installation and accommodation of engine movement.
PTFE oil pipes are comparatively stiffer, especially when reinforced. While they can still be bent to a certain radius, installation often requires more precise planning and proper fittings to avoid kinking or stress at connection points.
Vibration and Movement Tolerance
Rubber hoses naturally absorb vibration and movement, which can be beneficial in some applications. PTFE pipes rely more on proper mounting and support to manage vibration effectively.
Service Life and Long-Term Durability
A key difference between a low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipe and a rubber oil hose is expected service life. PTFE pipes are known for their long-term durability, often outlasting rubber hoses by several years under the same operating conditions.
Rubber hoses are considered consumable components in many systems. They require periodic inspection and replacement due to aging, heat exposure, and chemical attack.
Performance Comparison Table
| Feature | Low-Pressure PTFE Engine Oil Pipe | Rubber Oil Hose |
| Temperature Resistance | Very High | Moderate |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent | Good |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Service Life | Long | Shorter |
Application Scenarios and Use Cases
Low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipes are commonly used in high-performance engines, industrial machinery, and applications where temperature stability and oil cleanliness are critical. They are particularly suitable for long-term installations where maintenance access is limited.
Rubber oil hoses are more commonly found in standard automotive applications, small engines, and systems where flexibility, ease of installation, and lower upfront cost are prioritized.
Cost and Value Considerations
From a cost perspective, rubber oil hoses generally have a lower initial purchase price. However, their shorter lifespan and higher replacement frequency can increase long-term maintenance costs.
Low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipes typically involve a higher upfront investment, but their extended service life and consistent performance often provide better value over time, especially in demanding environments.
Choosing Between PTFE and Rubber Oil Solutions
The difference between a low-pressure PTFE engine oil pipe and a rubber oil hose ultimately comes down to application requirements. Factors such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, expected lifespan, and installation constraints should guide the decision.
For systems requiring maximum reliability, cleanliness, and long-term durability, PTFE oil pipes offer clear advantages. For simpler applications with limited thermal stress, rubber oil hoses remain a practical and economical solution.


 English
English Español
Español русский
русский